Each of us sooner or later faces the installation of new beautiful windows. How...
|
|
To protect your house from the penetration of groundwater, damp, capillary water, ... |
The floor slabs are inexpensive, convenient and indispensable, in many cases, ... |
Drowning with foam glass: step -by -step instructions

One of the best heat and soundproofing materials is foam glass. This insulation was created by Soviet scientists in the 30s, but due to the high cost and imperfect manufacturing technology, it was not widespread. After three decades, Canadians found practical use, where foam glass was used as a thermal insulation of the building. This material included this material relatively recently, when all flaws were taken into account and production costs were reduced. The article will talk about how to insulate a foam glass.
Content:
- What is a foam glass
- Foam glass characteristics
- Attention! Analogs
- Foam glass application
- Improving efficiency
- Installation of foam glass
What is a foam glass
- This inorganic thermal insulation material has a porous structure. In the process of production, the glass mass is heated at high temperatures, the added gaseous substance forms bubbles with a diameter of a millimeter to a centimeter. The porosity varies between 80-95%.
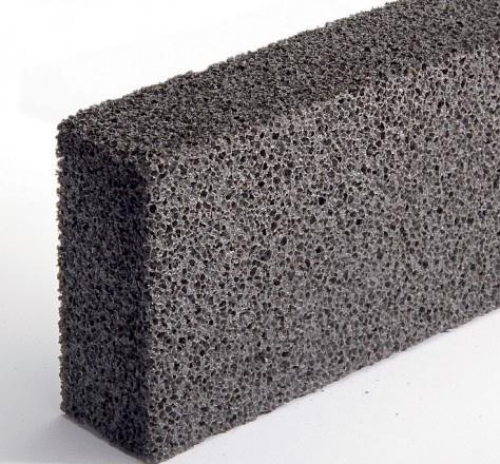
Foam -glass photo
- The color of the products can be different: cream, green or black. This property depends on the starting raw materials, because in production the crushed quartz, sodium sulfate, sedimentary rocks, and irrevocable fiberglass are used.
- The insulation is offered in the form of granules, plates and shaped products (pipes for pipes). Foam glass blocks, which may be the following sizes: are popular:
- length 200, 250, 400, 475 mm;
- width 125, 200, 250, 400 mm;
- thickness 80,100, 120 mm.
- Installation is carried out through mechanical fasteners, cement solutions, mastic and other adhesive compounds. The fixation method is selected depending on the type of surface (concrete, iron, wood).
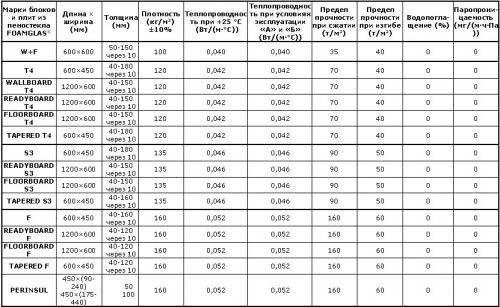
Foam glass characteristics
- This is light material, its density is 120-200 kg/m. cube.
- As for the compression strength limit, this indicator is very high and varies from 0.5 to 1.2 MPa.
- Thermal conductivity is even better than that of 0.06 W/m*with 0.09 W/m*C, respectively.
- The absorption index of sound waves with a plate of 100 mm thick is 50 dB, which provides increased comfort.
- The size of the sorption is negligible and does not exceed 4% of the volume.
- The temperature range for the use of material is very wide from -200 to +500C. At a higher temperature (from +540C), the plates begin to deform, but do not release toxic gases or vapors. Thermal resistance makes it possible to use foam glass at objects that are imposed on increased fire safety requirements.
- Chemical inertia is at a high level. The material does not interact with acids, alkalis, oil products and other aggressive environments.
Advantages of using foam glass
- In addition to high physical and technical characteristics, absolute environmental purity can be noted among advantages. The material is recommended for use in buildings with increased requirements of sanitary and hygienic conditions.
- The mats do not change their size throughout the entire period of service. Glass cells are not deformed under operational loads and seasonal temperature changes. Thus, the formation of cold bridges due to compression, sagging, swelling or shrinkage is not allowed.
- Foam glass is not subject to decay and development of corrosion processes. It is also not attractive to microorganisms, mold, fungi and rodents, which indicates biological resistance. Thanks to the above advantages, the service life of blocks is at least 100 years.
- Thermal insulation material is light in processing. It can be cut, drilled and sawed, while it does not form crumbs and cracks. It is combined with almost all types of building materials: cement, brick, iron surfaces, holds finishing compositions well.
Disadvantages of insulation with foam glass
- The main minus lies in high cost, because the manufacturing process itself is a complex technological task. For the production of insulation in the form of a shell, additional equipment is required, which entails an increase in the cost of the finished product.
- You can note another drawback of low resistance to shock loads. But this indicator is not critical, since the insulation is not subjected to such tests.
Attention! Analogs
- The market presents a cheaper analogue that is made of liquid glass. The finished product does not differ in strength and moisture resistance. At its core, this is a porous glue.
- The only plus of such material lies in a low cost, which can be 2, or even 3 times less than in penal products made of solid raw materials.
Foam glass application
Thanks to thermal insulating abilities, the material is used:
- in civil construction. It is widely used for thermal insulation of engineering communications. This material is equipped with warm floors, operated roofs, attic premises, basements, foundations. They are also insulated with internal and external walls;
- in sports facilities. Block and granular material is widely used in the construction of ice arenus, pools, playgrounds and other objects, to which special requirements are imposed;
- in industrial facilities. The foamed glassmass works to reduce operation costs due to high thermal resistance. Therefore, its use is relevant not only for ground, but also underground structures, for example, such as: buried tanks and other containers;
- in the national economy. The crushed stone from the foam glass provides the opportunity to build buildings on clay and swampy soils. It provides reliable thermal insulation of farms intended for breeding poultry, cattle, etc.;
- in the improvement of personalities. Foam -steel bulk material has found its application in the arrangement of greenhouses and greenhouses. Operational characteristics allow you to form a relief on the site, equip pedestrian paths, create gabions, use in drainage systems and so groundwater. They are also insulated with deepened containers.
Improving efficiency
- When choosing the thickness of the plates, it is necessary to take into account the thermal insulation properties of the material used for the construction of the house. So for external insulation of brick, concrete and silicate walls, foam -steel slabs 120 mm thick are used.
- For buildings made of wood, foam and expanded clay concrete blocks, this thermal insulation material with a thickness of 80-100 mm is suitable.
- Internal insulation work is carried out through foamed glass with a thickness of 60 mm. Plates are fixed using adhesive compounds, thin dowels and steel-shaped brackets.
- For the system, warm floor, foundation and inter -story (attic) ceilings use granular material. He will fill all the voids and provide the necessary thermal insulation. The calculation of the thickness of the layer is based on the temperature conditions of the region of residence.
Installation of foam glass
- For fastening mats, a special glue for foam glass is used. It is applied to the back and 2 side walls. Cement -containing solutions and bitumen compositions are evenly distributed around the perimeter.
- If there are minor bulges or hollows on the surface, then it is recommended to apply the adhesive mixture on the foam glass with slaps (at least 5 pieces per stove). With this method, glue consumption will increase, but the base will become as flat as possible.
- For wooden surfaces, special dowels are used. This is due to the fact that wood is subject to temperature expansion. In this connection, the plates should be fixed by a mechanical method that will allow the foam -steel blocks to move after the tree.
- Before installing the plates on vertical surfaces at the basement level, a horizontal bar is installed under the level. It can be a beam or a metal profile, if necessary, wedges are placed between the base and the rail. The empty space is filled with foam.
- The first row of insulation is installed on a profile acting as a support. After the adhesive composition is frozen, the support is dismantled. For reliability, the horizontal bar is best removed upon completion of all work.

- The foam -glass mats are mounted on the walls and inclined roofs from the bottom up, on horizontal surfaces (for example, on inter -story floors, foundations) in the direction of themselves, that is, from the far corner.
- The laying of foam -steel products is performed close to each other with the obligatory displacement of one row relative to the other (with the dressing of the seams). If, in addition to glue, it is planned to additionally use dowels, then their fasteners are carried out after completely drying the binder.
- Thermal insulation slabs around window or doorways, chimney and other elements are mounted with whole figures. The docking of blocks from foamed glass masses on the corner lines is not allowed.
Foam glass of styling technology
Knowing the method of fastening this material, you can easily and quickly perform insulation of any objects under construction. A competent arrangement of all layers will help increase the efficiency of thermal insulation.
Unique physical and technical properties can reduce the thickness of the pie and abandon the use of wind and moisture-proof membranes. Below is the most common use of foam -steel plates.
- A wall with a heavy cladding. Products made of foamed glass mass are glued to the reinforced concrete or brick surface. Additional fixation is carried out mechanically (4-5 dowels per stove). After the entire perimeter is laid, they switch to the installation of a metal profile intended for facing stone. This option is also applicable for the arrangement of the basement.
- Wall for plaster. Foam-steel mats are attached to brick masonry or walls erected from foam or aerated concrete blocks. Before applying the finishing material, the slabs are covered with an overlap with a net (at least 100 mm). It is fixed with plastered dowels with clamping washers. The thickness of the plaster layer can be up to 30 mm.
- Wall brick wall. The brick base is pasted with foam -steel slabs. Flexible connections are more convenient to insert after laying the insulation, and not before its installation. Next is the masonry of facing bricks. Here you can use granular material, which is covered between the main and facing wall as the latter is erected (the distance between masonry is at least 250 mm).
- Wall under the profiled sheet. Wall surfaces are pasted with foam glass. On top of them, a crate of wooden rails or a metal profile is equipped. The fasteners are selected depending on the material from which the walls are erected. Profiled sheets are installed according to the appropriate technology (from the bottom up and from left to right, overlapping horizontal and vertical levels).
- Internal walls (partitions). The work indoors is not much different from the external installation of the presented insulation. Also, insulation is attached to the surface, which is covered with a layer of plaster (you can mount a profile under drywall sheets).
- Roaling for roller materials. The reinforced concrete slab, if necessary, is covered with a bitumen-polymer primer, providing a high level of moisture protection. Next, hot mastic on a bituminous basis or adhesive solution is applied to the foam glass block and with slight pressure is fixed on the surface. The finished canvas is treated with hot bitumen. Using the burner, the waterproofing layer of the EPP is melted, and then the roll material such as ECP.
- Roof with a small slope for sheet coatings. Foam -steel blocks are glued to the overlap from reinforced concrete. You can use special adhesive compounds or bitumen mastics. Upon completion of the work, the surface of the foam glass is covered with hot bitumen-polymer mass. To increase the waterproofing of the roof, swimming materials are used. After solidification, a crate is performed corresponding to a particular roofing material.
- Wooden roof. A solid flooring is equipped on the rafters. On top of it, a layer of waterproofing materials on a bitumen basis is spread, the fastening of which is carried out mechanically. Next, foam glass is mounted, then waterproofing material. Now the surface is completely ready for laying any roofing material.
- Warming of floors with a foam glass. Foam -steel plates are densely laid out on top of the concrete base or a compacted layer of sand or cement. Here the thickness of the plate will depend on the alleged loads. Next, polyethylene is laid in 2 layers, and then the entire pie is filled with a sand and cement mixture. This basis is completely ready for arranging various finishing materials: linoleum, parquet, ceramic tiles, etc.
Foam -steel products have the characteristics necessary for the effective thermal insulation of buildings of any purpose. They combine: low heat transfer indicators, ease of installation, long-term operation, fire and bio resistance, environmental safety for both humans and structures.
Foam -glass video
Despite the high cost of this material, laying the foam -glass will pay off all expenses due to the absence of additional layers of the pie and thanks to the minimum amounts in heating accounts.










The rafters are equipped
A solid flooring is equipped on the rafters. On top of it, a layer of waterproofing materials on a bitumen basis is spread, the fastening of which is carried out mechanically. Next, foam glass is mounted, then waterproofing material. Now the surface is completely ready for laying any roofing material.
What BBred
How many crumbs from foam glass
How many crumbs from a foam glass will be required to warm a residential building with a wall thickness in a half-brick (12 cm), an ordinary hollow with a chamfer 250x120x65 mm GOST 530-2012 and in half a block of the foam concrete unit 19 cm. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the region 3.065.