Daching and suburban life always has one significant advantage ...
|
|
Even at the stage of designing the garage, they think about what kind of floor there will be. Sometimes from ... |
The constant increase in energy prices determines the fact that developers and ... |
Types of foundation and their technical characteristics

The choice of the right foundation is an even more important and responsible task than the construction of the house itself. Indeed, the durability of the entire structure will depend on the strength, stability and reliability of the base. That is why we will dwell in detail on what types of foundations are, in what cases they are used and on what soils.
- Ribbon foundation
- Column foundation
- Column-Lenthic foundation for TISE technology
- Pile foundation
- Home slab foundation
To choose the right home for the home, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors:
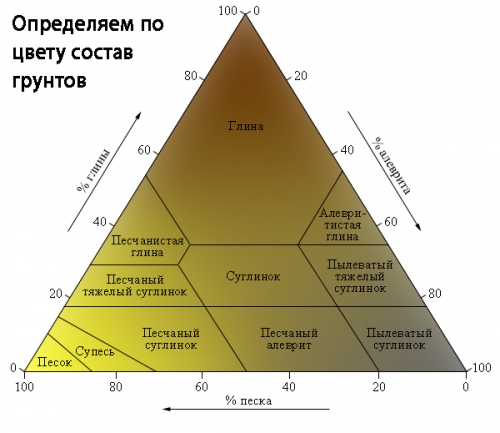
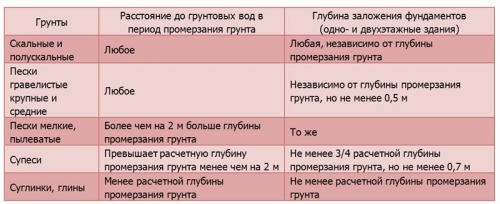
- The structure and condition of the soil on the site. Which foundation to choose is largely determined by the initial conditions of the site. There are fluffy soils that, when freezing or other change in atmospheric conditions, can move and expand, squeezing out the structure. Clips, sandy loam, loam, peat swamps include heaving soils. There are also non -gun soils that can serve as a rather strong basis for the foundation. These are sand, gravel and rocks.
- Groundwater. If the water is close, it can have a very negative impact on many types of foundations.
- The weight of the house, materialfrom which the walls will be built.
- Features of the architecture of the house: The presence of a basement or basement.
- Landscape features: even terrain or with a slope.
An important nuance is also a financial component. Typically, at least 25% of the cost of erecting the whole house is spent on the construction of a reliable foundation. And this is quite justified, given how important the strength and durability of the base is. It is strongly recommended to save on materials for the foundation, in the future this can lead to poor consequences.
So, below are the most common types of foundations for the home, cottage, baths, garage, extensions and other structures.
Ribbon foundation
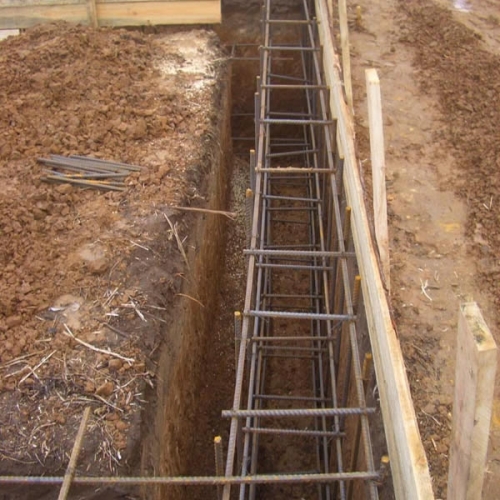
The most common view of the foundation is the strip foundation. It is a tape that passes under all supporting walls. In addition to the fact that the foundation tape is located around the entire perimeter of the house, it can also be under internal pieces or important heavy elements, for example, columns.
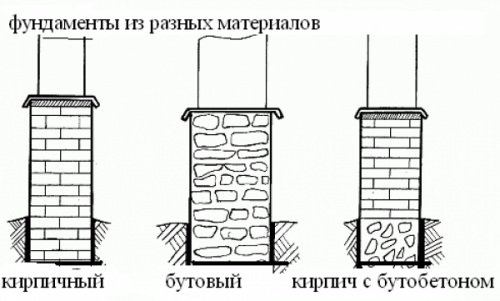
By the type of materials used, the strip foundation may be:
- Ward.
- Concrete.
- Buttone
- Reinforced concrete.
- Brick.
It can also be monolithic or prefabricated. For example, the foundation of concrete or reinforced concrete blocks of factory manufacturing is used if the construction of the house is planned to be completed in a short time for the summer months before rainy autumn or winter. In this case, there is no need to wait for the concrete to gain strength. The foundation of finished blocks can immediately after the arrangement serve as the basis for the construction of walls.
But I would also like to note that the non -low -alterated strip foundation has less strength, since the joints of the concrete blocks is a weak place. Water can seep in them, joints do not withstand the stresses on the bend, even in the case of reinforcing with a net, so that it is likely to break the foundation at the place of adjustment of the blocks.
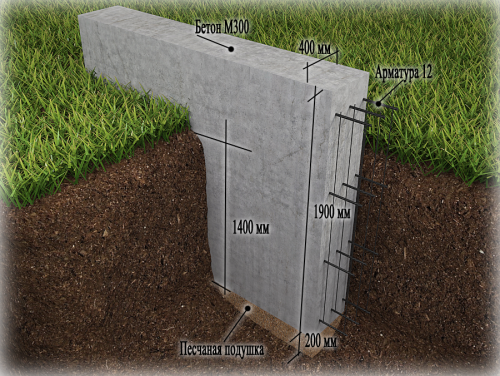
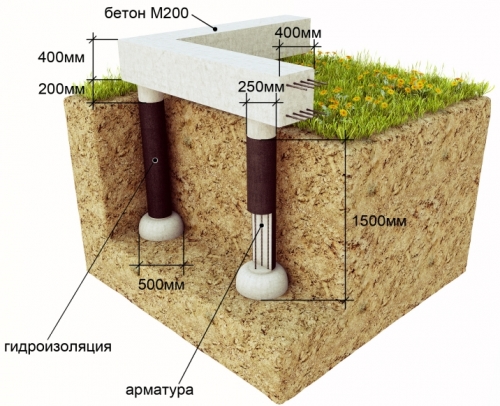
Monolithic foundation It is equipped using formwork. Bouto and bottle -made foundations are made in regions where a local cheap common material is boot. The width of the bottle foundation is usually 0.6 m if the masonry is made of a torn boot, and 0.5 m if the masonry is made of a bottle plate. Masonry of missile foundations is carried out on a concrete solution with mandatory ligation of vertical seams using a reinforcing grid.
Monolithic concrete and reinforced concrete foundation is the most common. Their width can be smaller than that of missiles, from 35 to 50 cm, depending on the thickness of the walls of the building and the bearing capacity of the soil. Typically, the width of the foundation is taken 20% more than the width of the wall.
The strip foundation can serve as the basis for such buildings:
- Brick house (from red or silicate brick).
- Reinforced concrete house of moderate severity.
- House made of stone.
- Log house.
- House from aerated concrete.
- Block buildings.
- Garages, baths, extensions, fences, etc.
Advantages of the strip foundation:
- The possibility of arranging a basement or basement.
- It withstands fairly large loads from heavy 2-3-storey buildings.
- You can equip heavy ceilings from concrete plates.
- Relative ease of construction, all work can be done independently.
The disadvantages of the strip foundation include the costs of materials: cement, gravel, sand and reinforcement. But the final result is worth it.
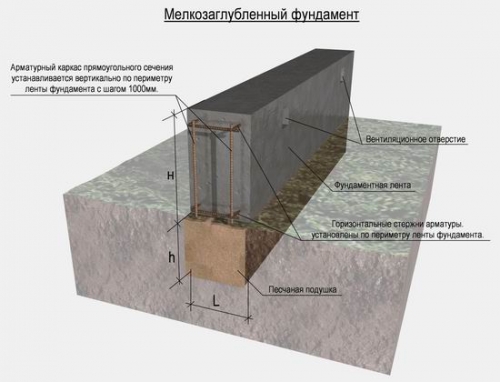
Small -sized strip foundation
There are two options for strip foundations in the depth of the laying: finely chased and buried.
The depth of laying a shallow foundation usually does not exceed 50 60 cm. It can be equipped on soils, which can serve as a strong base. These are the sand unpretated to fusion, crushed stone soil and stone rocks.
It is also important to know the level of groundwater. If it is lower than the level of freezing of the soil, then you can also equip a fine -trimmed foundation on clay soil and loam.
A fine -sized strip foundation is perfect as a base for light frame structures, garages, extensions, fences, wooden houses. Although for a one -story brick house you can also make an unscrupulous base.
The technology of arranging a fine -toed foundation can be described so:
- The trench is digging with a depth of 70 80 cm and a width of 50 60 cm.
- The bottom of the trench is compacted.
- A layer of crushed stone 30 cm is filled up at the bottom and is trimmed, and then a layer of sand 10 cm and also trim.
- A formwork is set inside the trench, the top of which should rise above the ground level by 30 50 cm.
- The walls of the future foundation must be protected from the influence of water, therefore, on the bottom of the trench and on the walls of the formwork, the waterproofing material roofing material, glassizol or any other roll material is attached.
- Inside the formwork, a reinforcing cage of a rod of 8 mm thick is placed.
- A concrete solution is poured on top.
- Concrete is compacted using a vibrator.
Do not neglect the crushed stone layer, since it serves as a kind of shock absorber. A well -prepared pillow of crushed stone and sand will eliminate the appearance of local drawdowns.
Important! This option of the foundation is not suitable if the site is uneven and has height changes, as well as for heavy stone buildings.
A brick finely chasseling strip foundation is an ordinary brick masonry made of burned brick, which does not absorb moisture. It can be equipped with wooden houses, extensions, garages and other mild structures.
Wheeled strip foundation
The depth of laying the so -called buried foundation is below the level of freezing of the soil. In different regions, this depth differs and is from 70 cm to 1.5 m or more. It can be equipped with any durable soil if the level of groundwater occurs below the level of freezing of the soil.
A buried strip foundation can be done on such soils:
- Sand.
- Clay.
- Loam.
- Suite.
- Rocky soil.
You can not make a strip foundation if:
- Ground waters are high. The foundation will freeze and collapse.
- Large height drops.
- Dog soil. Although there is an exception. If the peat layer is not too large, up to 1 m, then in this case it is removed to the entire depth to a strong litter base.
- Fanding fragile soil.
- The soil freezes too deep. It is impractical to spend money on the construction of such a deep foundation. For example, if the freezing depth exceeds 2 m, it makes sense to choose another type of foundation.
On insufficiently strong soils, you can make the tape wider and deeper. But this is only if the soil of average fluidity and at the bottom of the trench is still strong soil.
The technology for erecting a buried strip foundation is no different from the arrangement of a fine -trimmed foundation. The difference is only in the depths of the trench and the fact that the consumption of the material is much greater: more reinforcement and more concrete will be required. Also in the walls of the foundation, technological holes for pipelines and vents are provided.
The buried foundation is strong enough to withstand heavy stone buildings: brick, concrete, etc.That is why it is so popular among the inhabitants of our country.
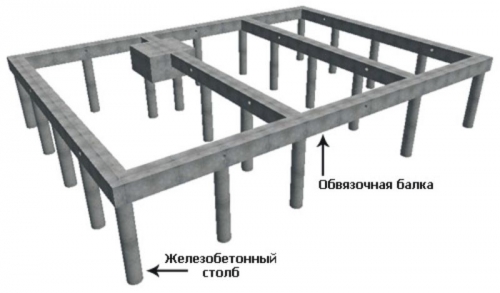
Column foundation
Column foundations are used in cases where the arrangement of a heavier strip foundation is inappropriate. For example, if the building is light and the load on the base is less normative. The column foundation is a pillars with a step of 2.5 3 m, located around the entire perimeter of the building under the supporting walls and under the inner pieces and places of intersection of the walls. On top of the pillars, a grillage is necessarily performed, which can be made of concrete, timber or channel.
The pillars themselves can be concrete, bottle, bottle, brick and wooden. The depth of the pillars is usually taken equal to the depth of freezing of the soil.
Columnar foundations can be used for:
- Wooden houses.
- Frame and shield houses.
- Extensions.
- Light houses made of aerated concrete.
Important! The columnar base is not suitable if it is planned to make a basement, basement or garage in the house. But this is the perfect option if the site has a slope. Then the pillars are deepened to dense soil.
Also, note that the columnar foundation can be used in cases where the laying of the strip foundation is inappropriate economically. For example, if the soil freezing depth is 4 5 m. In such cases, a columnar base with reinforced concrete grillage is equipped.
Wooden pillars They are used to build foundations extremely rarely, since they are short -lived. Before installing them in a well, wood is treated with various waterproofing materials and molds against mold. After processing, wooden pillars can last a maximum of 30 years. Typically, a wooden base is equipped with light wooden structures, such as baths, sheds, arbors.
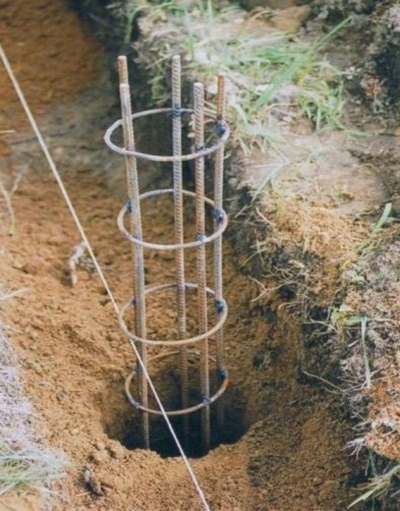
The technology of erecting a columnar foundation can be described so:
- Buryat wells for pillars to the required depth plus 20 30 cm. The diameter of the well is 25 cm.
- A layer of crushed stone 20 cm and a layer of sand 10 cm are filled on the bottom.
- After that, a roofing material rolled into a roll is lowered into the well, which will serve both formwork and waterproofing for pillars. Also sometimes used blanks in the form of steel or asbestos -cement pipes. The upper edge of such a formwork should rise above the ground by at least 30 cm.
- Inside the well, lower the reinforcing cage from a rod of 10 12 mm for vertical load -beers and 6 mm for horizontal ones. The reinforcement should rise above the formwork by 20 30 cm if it is planned to perform reinforced concrete grillage.
- Then, concrete is poured into the wells and tamped with a vibrator.

On top of the pillars you can equip a grillage of concrete, wooden beam or steel channel. In the technology of arranging a column foundation, an extremely important point to ensure the horizontal of the upper faces of the pillars so that they form a flat plane.
The dimensions of the column foundation depend on the material from which they are made. For brick, the width of the poles should be 50 55 cm. 25 cm are enough for reinforced concrete. Wooden logs are taken 25,28 cm in diameter. When arranging a bottle -column foundation, a width of 50 60 cm is taken.
Column-Lenthic foundation for TISE technology
A variety of columnar foundations, or rather a combined type of foundation, is a column-lental foundation for TISE technology. It is also called a pile-rosemer or pile-base foundation.
Recently, this type of foundation has gained widespread popularity, it has been equipped even under heavy stone houses in regions with cold winters and deep freezing of the soil. How durable they are, time will tell. In the meantime, they are recommended to be used in cases where the arrangement of the strip foundation is too costly.
The essence of the column-lental foundation is that the pillars are lowered below the depth of freezing of the soil, and a grillage is equipped in the upper layer of the soil in the form of a strip foundation.
The correct foundation for TISE technology is being built:
- The upper fertile soil is removed, then the trench is dug as for a strip foundation with a depth of 50 cm.
- At a distance of 1.5 2 m from each other, wells are drilled with a diameter of 25 cm for poles. Depth 1.5 m or equal to the depth of freezing of the soil in the region. Pillars must be located at all angles of the building and places of the walls of the walls.
- At the bottom of each well, an expanded heel with a diameter of 40 cm is performed.
- The heel is poured with a solution of concrete.
- Then, the formwork is lowered inside the well in the form of a roll of roofing material or asbestos pipe.
- A reinforcing frame is inserted inside, its upper edge should rise above the ground to the full height of the future foundation.
- A wooden formwork is equipped along the perimeter of the trenches, which provide for technological holes for pipes and communications.
- Inside the reinforcing frame is inserted and it is associated with a frame sticking out of the wells.
- After all reinforcement elements are interconnected, you can start pouring concrete solution.
- First, pillars are poured and concrete carefully compacted with deep vibrators.
- Then, without a break, the tape is poured and concrete is also compacted.
After pouring, concrete gains strength within 28 30 days. After this time, you can continue construction.
The column-lental foundation is not recommended to equip in marshy areas, on peat bogs. During operation, the separation of concrete pillars from the foundation tape or skew of the entire support is likely. But if the soil is dense, the foundation of this type can save a lot of money.
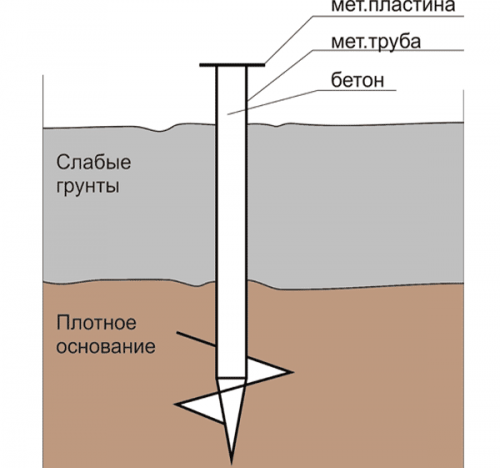
Pile foundation
If the area is weakly squeezed by the soil, then the pile foundation is equipped. Also, if the achievement of solid soils of the natural base under peatants is inappropriate due to their large laying depth of 4 6 m, a pile foundation is clogged as a base for the building.
Among other things, pile foundations are allowed to equip for buildings on solid soils, if it is economically justified.
By the method of transmitting and distributing loads on the soil, two types of piles are distinguished:
- Hanging piles Do not reach a solid soil of the natural basis. They seem to hang in a light compressed breed and transfer the load on it over its entire vertical surface. Usually their end is a screw thread that is well held in the ground.
- Standing pilesor the piles pass through the weak soils to a solid base and rely on it with their ends.
According to the method of arrangement, screw piles are divided into clogging and stuffed. Cutted piles They score into the soil with special heavy equipment, at the same time as the pile, the soil around it occurs, which ensures greater reliability.
Stunk piles They are equipped at the construction site using the same technology as the pillars for the column foundation.
Piles can be concrete, reinforced concrete, metal and wooden.
A screw foundation, as a rule, is made of steel piles with threads at the end, they are screwed into light soil. The grillage is equipped from above, the material of which depends on the severity of the structure and material of the walls. For a wooden house, a grillage is enough in the form of a mortgage beam.
Pile and pile-screw foundations can be equipped with peat soils, in cases where the site has a strong slope, on floats, swamps, and subsidence soils. An indicator for the use of piles as a support is low strength, porosity and excessive moisture in the soil on the site.
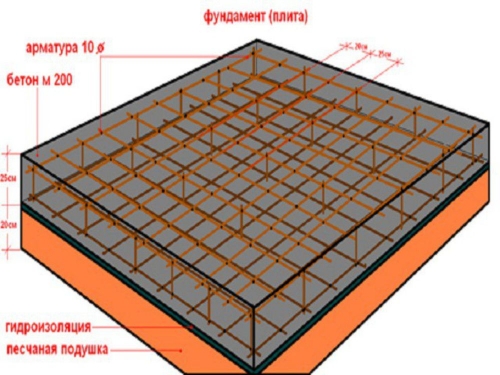
Home slab foundation
A solid or slab foundation is a slabs under the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe structure. It is equipped in cases where the load from the building is significant, and the soil of the base is weak and is not able to withstand it. For example, if a plot on a drained swamp, a soft porous peat is not able to withstand the weight of the house, it will compress, move under its weight. If you equip the strip foundation, it is likely that it will simply break or skew it, part of the house can fail.
The slab foundation is good because it will move and travel with the ground soil. The house will remain intact.
The technology of arranging a slab foundation can be described so:
- The foundation pit is dug over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe building. The depth of the pit depends on whether it is planned to make a basement and basement. Consider the option without a basement. In this case, the depth of the pit should be 50 cm.
- The bottom of the pit is thoroughly compacted.
- Then pour a coat of crushed stone 20 cm, trim.
- Then a layer of sand 10 cm and also trim.
- A layer of waterproofing material is spread on top, the edges of which are trained on the walls of the pit.
- Equip the formwork around the perimeter of the pit. Height is usually not more than 20 cm above the ground level.
- A reinforcing frame from a rod of 12 16 mm is equipped inside the pit. It takes a lot of material for its manufacture.
- The reinforcing cage should be located in the thickness of the concrete, so chairs are placed under it 3 cm high.
- Concrete is poured. Be sure to without interruption, so a mixer with ready -made concrete is ordered for the site.
- Concrete is compacted using vibrators.
Plaet foundations are sometimes called floating, as they are able to move along with the soil. They can be equipped on such grounds: clay, subsidence soils, swampy terrain, floats, peat soils, and fluffy soils. On hard grounds, the slab foundation is unprofitable.
In conclusion, I would like to give several recommendations. If the site has high groundwater, it is better to equip a slab foundation, small -sized or pile strip. If the water level is so high that it is likely to get wet even of an unsuccessful foundation, then it is necessary to perform high -quality drainage around the house and take the water into a grated ditch or well. It is extremely undesirable for the reinforced concrete foundation to get wet. Dry soil is considered if the groundwater level is below the level of freezing of the soil. As a rule, in such cases, you can equip any foundation.
















http://arzan102.ru/fundament
http://arzan102.ru/fundamentnye-raboty
Detailed information.
Detailed information that gives a general understanding of the foundation device. Thanks for your work.
There is such a channel dedicated
There is such a channel dedicated to the topic of foundations where they talk about the advantages and disadvantages of different types.
https: //www.youtube.com/channel/uckcigosdtnxfaaenjxlwc5a/videos? View_as \u003d ...